Describe the Equipment Used in Extraoral Imaging
Our equipment is designed to promote proper posture for doctors assistants and patients alike while helping to provide the workflow that best suits your practice needs. The lateral cephalometric projection is used to evaluate facial growth and development trauma disease and developmental abnormalities.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of.
. Define extraoral radiography and apply extraoral radiographic techniques. Lead plate with a small round or rectangular opening in the middle. The extraoral films are used in combination with the cassettes and the intensifying screens.
Tell me when Its Available. Provide the highest level of care and get the most efficiencies from your workflows with 2D and 3D technology. Describe the purposes and uses of extraoral imaging.
Staff didnt hold film in the pts mouth during exposure-use suitable film holder. Lead plate with an opening in the shape of a narrow vertical slit. Extraoral film equipment.
1A standard intraoral x-ray machine may be used for a variety of extraoral projections. Extraoral images are particularly beneficial for patients requiring orthodontic treatment dental implants and oral surgical procedures. Prepare a patient for a panoramic x-ray.
There are many type of extraoral radiographs. Prepare the equipment necessary for a panoramic image. Extraoral radiographs are very useful for evaluating large areas of the skull and jaws but are not adequate for detection of subtle changes such as the early stages of dental caries or periodontal disease.
Created using patented software-driven SCARA technology Planmeca ProMax 3D provides dependable 2D3D imaging with versatile programs and volume sizes to accommodate a wide range of clinical needs. Learning Objective 5 Panoramic imaging and Cone Beam Computed Tomography Describe the purpose and uses of panoramic imaging. 3The panoramic tubehead is used in conjunction with a special extension arm and a device known as a cephalostat or craniostat.
Identify the specific purpose of each of the extraoral film projections. The collimator used in the panormaic x-ray machine is a lead plate with an opening shaped like a narrow verticle slit. The vertical angulation of the panoramic tubehead is not adjustable.
Describe the equipment used in extraoral imaging. Collimator trestricts the size and shape of the x-ray beam. Extraoral Imaging Techniques 1.
Identify the core intraoral imaging techniques and list the basic rules for each. Prepare the equipment and the patient for a panoramic procedure and produce an image. Identify and discuss anatomical landmarks for proper mounting of radiographs as.
Identify and describe the equipment used in extraoral. If you are a doctor who looks at the precision of this equipment and thinks its overkill for the patients you see it may be time to rethink that assumption. Describe the equipment used in panoramic imaging.
Describe the advantages of three-dimensional 3D imaging. Various extraoral imaging techniques used in dentistry. 2Special head positioning and beam alignment devices can be added.
The tubehead rotates behind the patients head. Intraoral Imaging 11 Hours Identify the components in preparing a patient for dental imaging. Field diameter at the end of the cone should not exceed 6cm.
Describe the components and purpose of quality assurance. List the steps for patient preparation and positioning in panoramic imaging. Describe the purpose and uses of panoramic radiography.
SARBAJIT HALDER DEPARTMENT OF. To prepare the patient for panoramic imaging explain the procedure to the patient as him or her to remove all metal objects from head and. Planmeca ProMax 3D Imaging Units.
Most extraoral exposures use screen film place in cassette that has an intensifying screen grid a device used to reduce the amount of scatter radiation that reaches extraoral film during exposure. The film rotates in front of the patients head. Midmark Extraoral Imaging System.
Describe the steps for patent preparation and positioning in panoramic imaging. X-ray beam emerges from teh panoramic tubehead through the collimator as a narrow band. Describe the equipment used in panoramic radiography.
Define infection control protocol. Extraoral radiographs do not show the details as well as intraoral films. PACS CR DR Digital Systems.
A special device used to hold the intensifyin. Describe the equipment used in extraoral imaging. Ad Customized Solutions For Enhanced Patient Experience.
Pronounce define and spell the Key Terms. G screen and the extraoral film is available in various sizes that correspond the. Describe the steps for patient positioning in panoramic radiography.
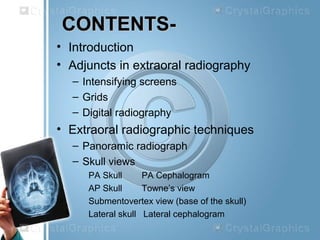
Patient Staff X-ray unit should be equipped with a field defining spacer cone which allow a minimum focus-skin distance of 20 cm for 60kVp and 10 cm for. NEW HORIZON DENTAL COLLEGE AND RESEARCH INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL MEDICINE DIAGNOSIS ORALAND MAXILLOFACIAL RADIOLOGY SEMINAR ON EXTRAORAL IMAGING TECHNIQUES SUBMITTED BY. The equipment used in extra oral imaging are the x-ray unit film intensifying screens cassette and grid.
Customize your workflow with open architecture which allows for seamless integration with most third-party products. A lateral cephalograph is a sagittal projection of the skull that includes both the hard and soft tissues. The equipment used in panoramic imaging are the panoramic x-ray unit screen film intensifying screens and cassette.
3D dental imaging is rapidly becoming the standard of care in all of dentistry not just specialty fields. What type of additional images are no longer necessary to supplement a panoramic radiography when the new full features digital panoramic units are. Typical extraoral x-ray images include panoramic cephalometric and cone beam computed tomography CBCT projections.

Examples Of Intraoral And Extraoral Bitewing Radiographs A Intraoral Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Describe the Equipment Used in Extraoral Imaging"
Post a Comment